There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Effective risk management in banking is crucial in today’s volatile financial landscape. It is a survival strategy to maintain trust, profitability, and stability. Globally, there are multiple banking risks - credit defaults, market swings, cyberattacks, and regulatory shifts - which can trigger ripple effects across economies.
These instances show that modern banks face complex, interlinked risks. A robust risk management in banks helps with financial resilience, compliance with the guidelines, systemic stability, and protecting customer confidence.
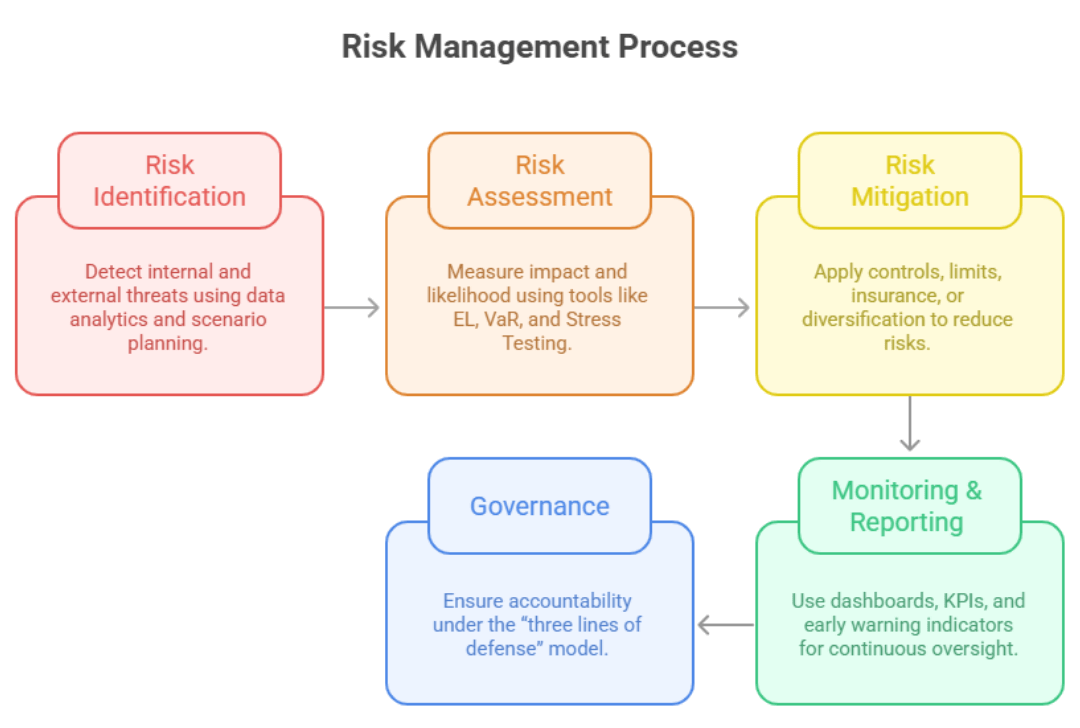
Risk management in banking refers to the structured process of identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring potential threats that can impact a bank’s earnings, capital, or reputation. Risk management in banks ensures that institutions balance risk and reward while staying compliant with frameworks like Basel III and ISO 31000.
To implement effective risk management, banks must follow a disciplined, cyclical process:
Banks worldwide face a wide range of risks, including traditional and new challenges emerging from technology and globalization.
Credit Risk occurs when borrowers default on loans or interest payments. It is a major cause of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in Indian banks.
If you’d like to explore these strategies in depth, check out our comprehensive course on Credit Risk Management.
Market risk refers to potential losses arising from fluctuations in market variables such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and equity prices.
Liquidity risk occurs when a bank is unable to meet its financial obligations as they fall due, without incurring unacceptable losses.
Operational risk stems from internal process failures, human errors, system breakdowns, or external events such as fraud.
Compliance and legal risk arises from non-adherence to laws, regulations, or internal policies, leading to penalties or reputational damage.
Reputational risk refers to the loss of public trust caused by unethical behavior, governance failures, or poor crisis management.
Strategic risk emerges when poor business decisions or external shifts, such as new fintech competitors or regulatory changes, undermine a bank’s business model.
With the rapid digitization of Indian banking and the surge in UPI transactions, cyber and technology risks have become critical. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams have targeted major Indian banks and fintechs alike.
As financial systems become more globally interconnected, risk management has evolved from a regulatory function into a vital pillar of sustainable banking strategy. From credit to cyber risks, the modern banking environment demands foresight, resilience, and continuous learning. By adopting global frameworks like ISO 31000, Basel III, and COSO ERM, and leveraging technology for proactive mitigation, banks can protect stakeholder value, enhance governance, and prepare for the uncertainties of tomorrow.
If you found this blog insightful and want to dive deeper into implementation-focused learning, check out our Risk Management in Banking courses. Our courses are designed by risk professionals and include: