There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Risk management is no longer a support function focused only on compliance or loss prevention. As risks become more complex, interconnected, and regulated, organizations require structured frameworks that guide decision-making across strategy, operations, technology, and governance.
By 2026, professionals who understand how to apply globally recognized risk management frameworks will be better positioned to manage uncertainty, support leadership decisions, and meet regulatory expectations. Frameworks provide a common language for risk, align stakeholders, and transform risk management from a checklist exercise into a strategic capability.
This blog outlines the most important risk management frameworks to learn in 2026 and explains why each remains relevant for professionals across industries.
Also Read: Future Job Roles in 2026: What They Look Like and What Skills They Need
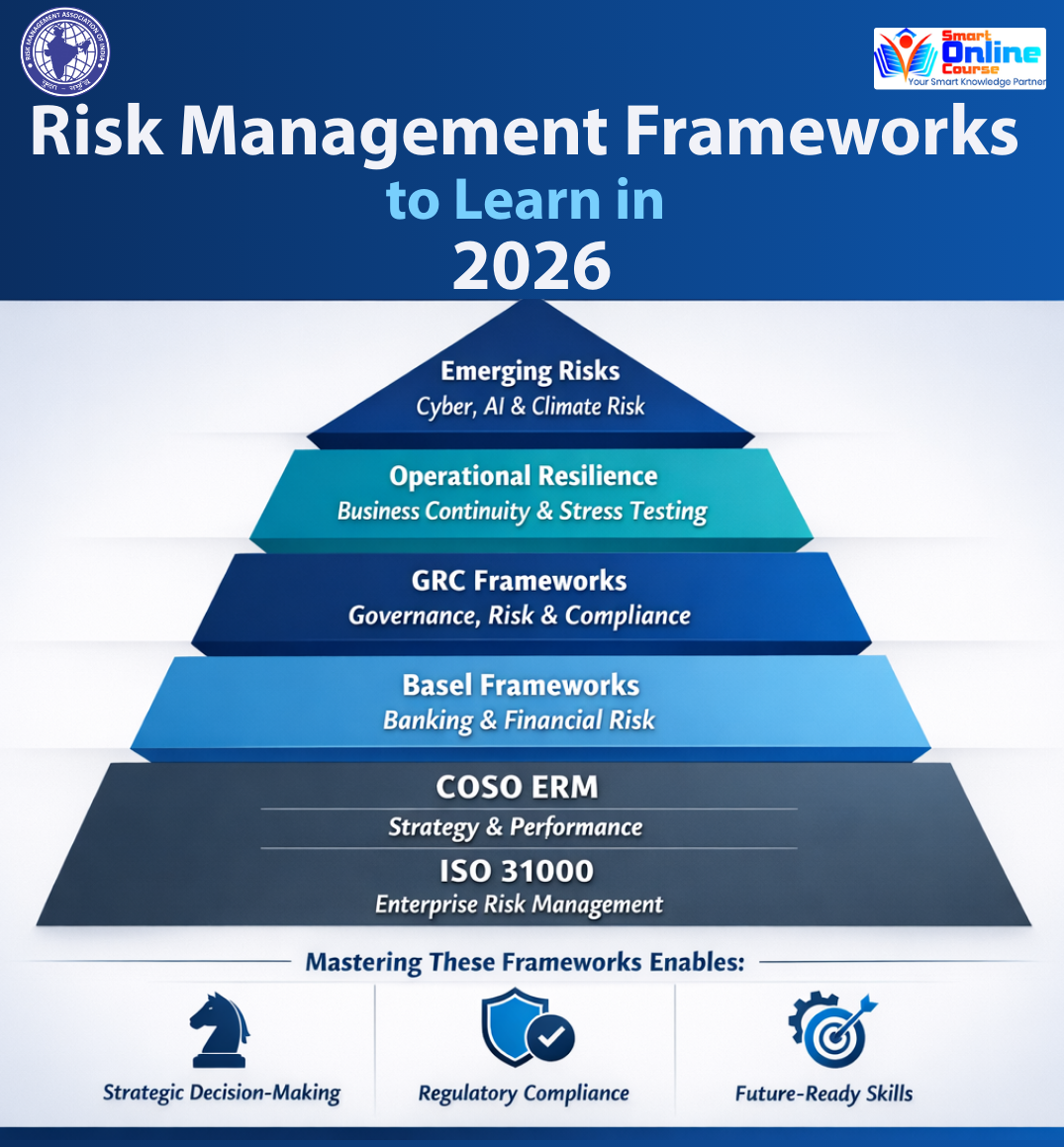
ISO 31000 continues to serve as the global foundation for enterprise risk management. It provides principles, a framework, and a process that can be applied to any organization, regardless of size or sector.
The strength of ISO 31000 lies in its flexibility. It does not prescribe controls or risk thresholds. Instead, it focuses on embedding risk management into governance, leadership, planning, and operations. This makes it particularly valuable for organizations seeking consistency in risk thinking without rigid compliance constraints.
For professionals, learning ISO 31000 builds a strong conceptual base. It improves the ability to identify, assess, treat, and monitor risks while aligning risk decisions with organizational objectives.
The COSO Enterprise Risk Management framework emphasizes the integration of risk with strategy and performance. Unlike traditional risk approaches that focus on risk registers, COSO ERM encourages organizations to consider risk at the point where strategic decisions are made.
COSO ERM is widely adopted by boards, senior management, and internal audit functions. It links risk appetite, strategy formulation, and performance measurement, making it highly relevant for leadership and decision-makers.
Professionals who understand COSO ERM gain the ability to frame risk as a value-protecting and value-creating discipline. This makes the framework particularly relevant for roles in corporate risk, internal audit, finance, and enterprise governance.
Many professionals understand risk frameworks but struggle to apply them in practice. Translating these frameworks into risk assessments, governance structures, and decision support is what sets strategic risk teams apart.
Smart Online Course offers structured, application-focused learning that helps professionals move from framework awareness to real-world implementation capability.
Basel frameworks remain essential for professionals working in banking and financial services. Basel III and its evolving updates focus on capital adequacy, credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
Regulatory scrutiny in financial institutions continues to intensify, making Basel knowledge critical for compliance, risk modelling, and supervisory engagement. These frameworks also influence enterprise risk practices beyond banking, particularly in large financial and regulated organizations.
Learning Basel frameworks equips professionals with a strong understanding of quantitative risk assessment, regulatory capital, stress testing, and risk governance within highly regulated environments.
Siloed compliance functions are increasingly ineffective in managing modern risk. Governance, risk, and compliance frameworks aim to integrate policies, controls, assurance, and reporting into a unified structure.
GRC frameworks support better visibility across risk domains, reduce duplication, and improve accountability. They are particularly valuable in organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions with complex regulatory requirements.
Professionals skilled in GRC frameworks can design integrated risk and compliance architectures that support business objectives while maintaining regulatory discipline.
Operational risk and resilience frameworks have gained prominence following global disruptions, supply chain shocks, and technology failures. Business continuity management, operational resilience, and stress testing frameworks help organizations prepare for severe but plausible disruptions.
Regulators increasingly expect organizations to demonstrate not just recovery capabilities but also the ability to continue critical services during disruptions. This has elevated operational resilience from an operational issue to a board-level concern.
Learning these frameworks enables professionals to design response strategies, test resilience, and align operational risk management with enterprise objectives.
Several emerging risk domains are reshaping risk management priorities:
Understanding frameworks that address these emerging risks will be essential for future-ready risk professionals.
The right framework depends on your role, industry, and career stage.
Selecting frameworks strategically allows professionals to build layered expertise rather than fragmented knowledge.
Risk management frameworks are not theoretical checklists. They are practical tools that help organizations anticipate uncertainty, protect value, and support strategic decisions. As regulatory expectations and risk complexity increase, professionals who can apply these frameworks effectively will remain in high demand.
Smart Online Course, in association with RMAI, offers structured, industry-aligned learning paths that help professionals master globally recognized risk management frameworks and apply them in real-world scenarios. Investing in framework-based learning today builds the competence required to manage the risks of 2026 and beyond.
👉 Browse relevant courses here: Click Here